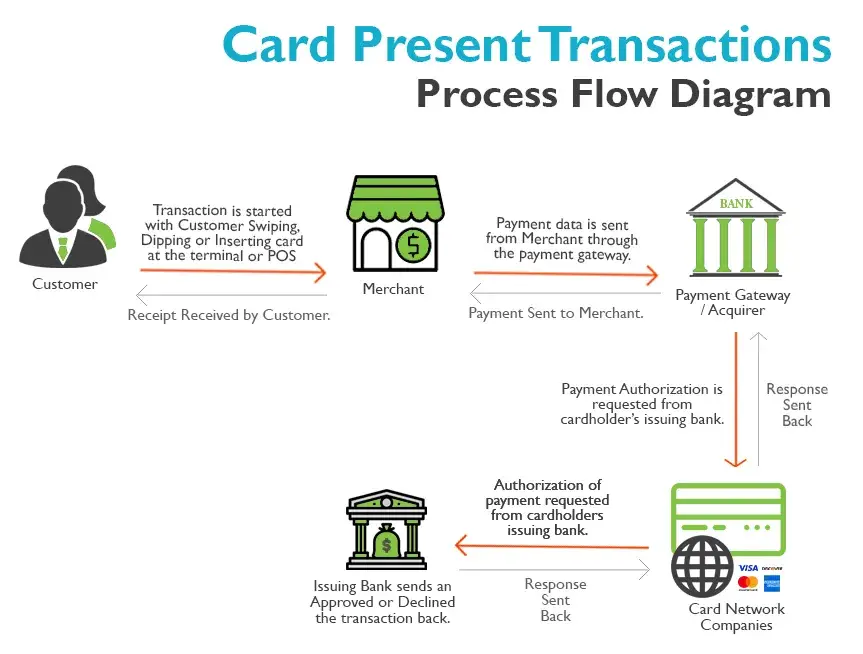
What is a Card Present Transaction?
A Card Present transaction occurs when a payment card is physically present during a purchase. This type of transaction is typical for in-store or point-of-sale (POS) purchases where the customer either swipes, dips, or taps their card on a terminal. Card Present transactions are usually considered safer due to the physical presence of the card, and they often require additional authentication methods such as PIN entry or signature verification.
Key Characteristics of Card Present Transactions:
- In-person Verification: Customer and card are both physically present.
- EMV Chip Technology: Many card present transactions use chip cards, which offer added security through encryption.
- Lower Fraud Risk: Physical presence and additional verification reduce the likelihood of fraud.
- Lower Processing Fees: Because of the reduced risk, Card Present transactions often incur lower interchange fees compared to CNP transactions.
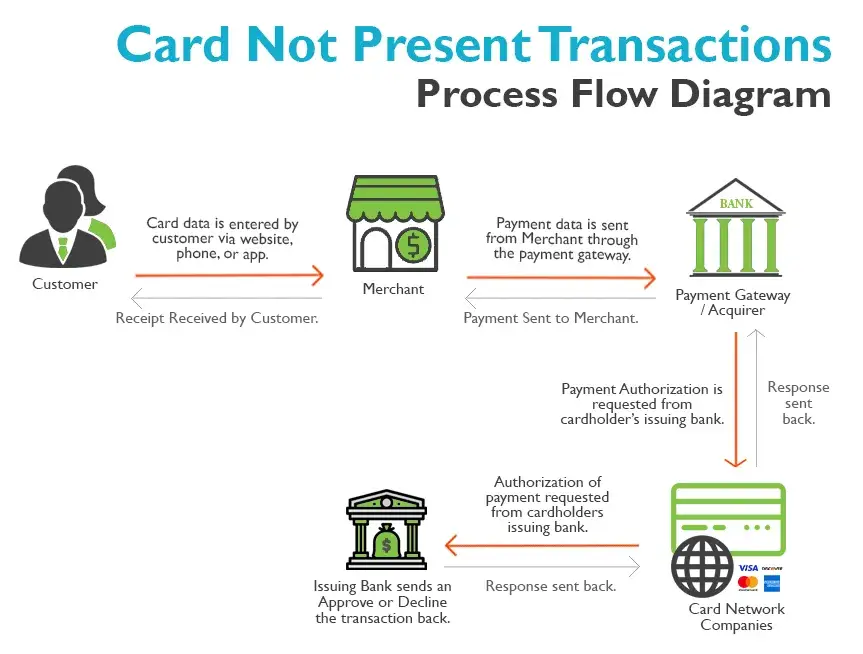
What is a Card Not Present Transaction?
A card-not-present transaction, as the name suggests, happens when neither the cardholder nor the card is physically present at the point of sale. These transactions typically occur online, over the phone, or through mail orders. Because there’s no way to physically verify the card, card-not-present transactions carry a higher risk of fraud and may require stronger security measures.
Key Characteristics of Card Not Present Transactions:
- Higher Fraud Risk: The lack of physical presence increases the likelihood of fraudulent transactions.
- Higher Fees: Due to increased risk, processing fees for CNP transactions are generally higher.
- Advanced Security Required: Strong security measures such as CVV, 3D Secure, and tokenization are recommended for CNP transactions.
Pros and Cons of Card Present and Card not present Transactions
Card-Present
Card-Not-Present
Security Considerations for Card Not Present Transactions
- Address Verification System (AVS): Confirms if the billing address matches the cardholder’s records.
- Card Verification Value (CVV): Adds an additional layer by requiring the three or four-digit security code.
- Tokenization: Replaces card data with a unique identifier to secure card details during processing.
- 3D Secure Authentication: This adds another step to authenticating customers during online transactions.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
For businesses, the choice between Card Present and card not present transactions often depends on their operational model. Traditional brick-and-mortar stores are more likely to rely on Card Present systems, while e-commerce platforms, subscription services, and phone order-based companies primarily handle CNP transactions.
Many businesses operate in a hybrid environment, accepting both CP and CNP payments. In such cases, it’s crucial to have a versatile payment solution that can handle both transaction types seamlessly. Solutions like Merchant First can provide businesses with the flexibility to manage and secure both card-present and card-not-present payments, offering features such as integrated EMV technology for in-store payments and advanced digital security tools for CNP transactions.
Optimize Your Card-Present and Card-Not-Present Transactions Today!
Understanding the differences between card-present and card-not-present transactions is essential for any business that accepts credit or debit card payments. Each transaction type has its own unique advantages and challenges, from security concerns to cost considerations. With the right payment solution, you can optimize your processes, reduce fraud, and deliver a seamless experience for your customers.
Ready to streamline your payment processing? Contact Merchant First today to learn more about how we can help your business manage card-present and card-not-present transactions efficiently and securely.